To achieve lower emissions on mobile offshore platforms, oil & gas companies look to engineering consulting teams to learn how to integrate renewable systems into existing power generation systems. Implementing renewable power generation and battery storage on FPSOs (floating production, storage, and offloading vessels) requires careful study to maintain safety and reliability. In this project, Power Products took the challenge and used ETAP to address the technical feasibility.

Power Projects India provides independent, customized power system consulting services in India and other global markets, across many industries, including renewables, offshore oil & gas, data centers, manufacturing, transmission & distribution, and water & wastewater. Established in 2006, Power Projects' expertise covers every aspect of electrical engineering, including power system studies, consulting services, detailed engineering, design engineering, and technical support.
Location: Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Year: 2024
Objectives and methods
Integrate wind turbine generators (WTGs) and BESS into a FPSO power system
For the existing system:
Identify methods to limit short-circuit currents due to multiple gas turbines operating in parallel
Prevent large-motor starting transients which cause voltage dips and potential relay miscoordination
Study harmonic distortion from variable-frequency drives and long 13.8 kV cables
Consider the frequency response to the sudden outage of a generator
Address the protection challenges due to varying short circuit current and fault-limiting device response
Integration of renewable systems:
Determine the optimal integration of wind turbines and BESS
Achieve a 25 % renewable energy share
Limit excess export to ≤ 5 %
Study wind variation and load variation
Consider the stress on the gas turbine generators, spinning reserve and optimal battery sizing for operational stability and safety
Payback period must be achieved in under 10 years
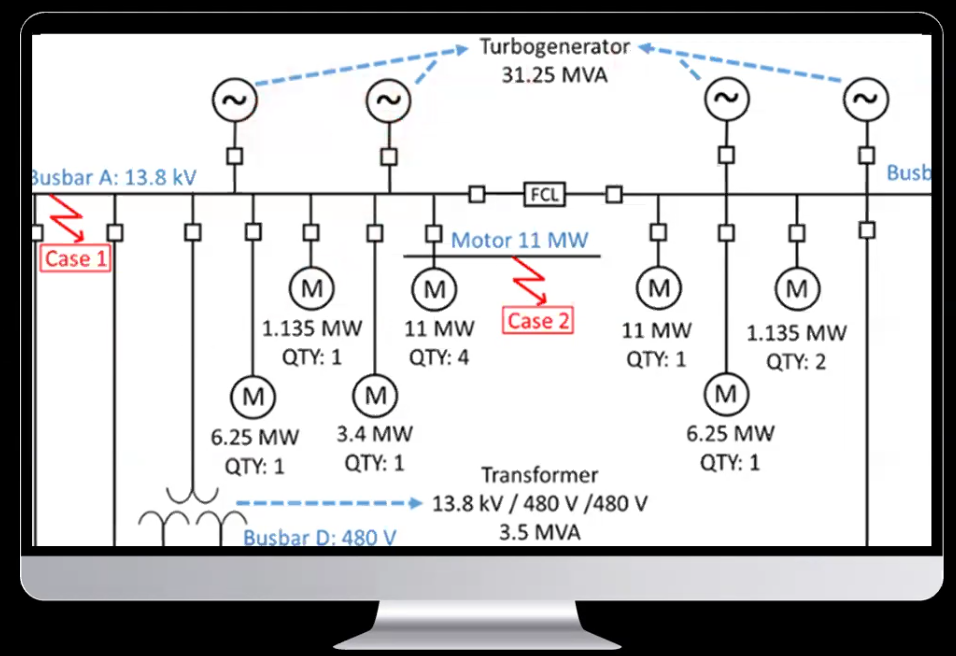
An existing FPSO typically uses a 100% conventional generator by a gas-powered turbine, with a peak demand of 70 MW powered by four 25 MW gas turbine generators. System voltage variations are 13.8 kV for the large capacity of the connected generators, 4.16 kV for other motors, and 0.48 kV for further sub-distribution levels.
Traditionally, FPSO power systems encounter several challenges, including transformer energization, motor starting, protection coordination, and short-circuit current limitations. Transformer energization and motor starting may result in very poor voltage, which will also affect the rest of the system. Additionally, protection coordination between multiple generators and loads is complex, requiring careful design to ensure proper fault detection and isolation. To ensure operational reliability, FPSO power systems are typically designed with an N+1 configuration, maintaining a spinning reserve to handle sudden load changes or generator failures.
By incorporating renewable energy through wind turbine generators (WTGs), the operational carbon footprint of FPSOs can be significantly reduced. The introduction of WTGs to reduce carbon emissions adds further complexity to the system. The intermittent and variable nature of wind energy affects both the power quality and the dynamic behavior of the system, making it challenging to maintain stability, manage spinning reserves, and coordinate protection schemes effectively. Several energy evaluation scenarios were identified for the WTGs over time, and the technical feasibility was studied for the proposed system.
Products used
ETAP Power Simulator - Comprehensive electrical network design and analysis, including:
- Unified Electrical Digital Twin – To build and analyze a virtual representation of the existing and proposed updates to the electrical power system
- Load Flow Analysis
- Short Circuit Analysis
- Motor Acceleration Studies
- Transient Stability (co-simulation with PSCAD)
- Voltage Ride Through
- Protection and Coordination
- Transformer Energization
What we delivered
- ETAP analysis identified areas for improvement in the existing system.
- The studies ensured validation of power quality and safety compliance for the integration of WTGs and BESS for integrated renewable power generation.
- These studies ensured the technical feasibility of the proposed system to perform its task effectively and efficiently.
- The ETAP design to operation platform will provide a smooth transition for further studies, such as time-domain load flow, and implementation of ETAP real-time solutions for optimization using ETAP Time-Domain Load Flow, ETAP SCADA and ETAP Microgrid Controller.
Outcomes
Future-Ready Power System for FPSOs to Meet Sustainability Goals
- A system was identified that provides enhanced reliability and safety by using ETAP for validation of all operating conditions
- The design met the goal of reduced carbon emissions with up to 25% renewable integration and less than 5% energy wasted
- An optimized BESS capacity was determined that would ensure spinning reserve and frequency support under high wind variability
- The engineering team implemented a faster design process thanks to the use of ETAP Digital Twin for comprehensive power system analysis, by incorporating data into ETAP from other equipment simulation and analysis tools.
- The project design can be further optimized, using the ETAP Digital Twin single platform solution for time-domain load flow and harmonic mitigation, ETAP Real Time and ETAP Microgrid Controller.
1
Videos
Learn how Power Products integrates wind turbines for optimal BESS sizing for FPSO using ETAP
The transition towards sustainable energy sources is driving innovative solutions in the offshore oil and gas industry. The presentation delves into the integration of a Wind Turbine Generator (WTG) into an existing Floating Production Storage and Offloading (FPSO) vessel to reduce carbon emissions. The technical and operational challenges of this integration are discussed, including load balancing, intermittency of wind energy, transformer energization, motor starting, protection coordination, and maintaining operational reliability. The study utilizes simulations with tools like HOMERPRO, ETAP, and PSCAD to assess the technical feasibility of integrating the WTG and Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) into the FPSO power system. Various studies, including load flow, short circuit, motor acceleration, transient stability, voltage ride through, harmonic analysis, protection coordination, and transformer energization are conducted to ensure the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed system. There is great potential for reducing the operational carbon footprint of FPSOs by incorporating renewable energy sources and using software simulations to address the complexities and considerations involved in such integration.
Solutions
Packages/Products
- Analysis
- Design
- Energy & Chemicals
- Engineering Consulting
- ETAP
- India
- Renewables
- Simulation